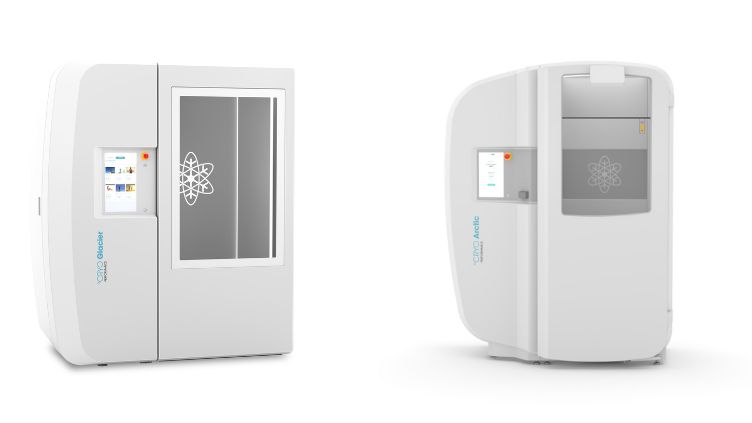
Difference Between a Nitrogen vs Electric Powered Whole-Body Chamber
Cryotherapy chambers, which are used for whole-body cryotherapy (WBC), can be powered by either liquid nitrogen or electricity. Each type has its own advantages and disadvantages. Here’s a comparison of nitrogen-powered cryotherapy chamber ( °CRYO Arctic) and electric cryotherapy chamber (°CRYO Glacier):
°CRYO Arctic (Nitrogen-Powered Cryotherapy Chamber)
Quick Info:
-
Safest and most effective Cryotherapy Chamber in the world
-
No Direct Injection of Nitrogen Vapor on skin.
Selling Points
-
Rapid Cooling: Liquid nitrogen can quickly reduce the temperature, often reaching as low as -140°C/-220°F in under 4 minutes!
-
Lower Initial Cost: Typically, nitrogen-powered units have a lower initial cost compared to electric units.
-
Portability: Generally more portable since they don’t require as much electrical infrastructure.
-
Sessions: Can easily do 8-12 sessions in an hour!
-
Safety: There is no contact with nitrogen, clients only breathe 100% pure breathable air.
Things to Consider:
-
Ongoing Costs: Regular supply of liquid nitrogen is required, leading to ongoing operational costs.
-
Safety: Handling and storing liquid nitrogen requires strict safety measures
-
Ventilation Requirements: Adequate ventilation is necessary to avoid the buildup of nitrogen gas, which can displace oxygen in the room and pose asphyxiation hazards.
°CRYO Glacier (Electric Cryotherapy Chamber)
Quick Info:
-
Fastest cooling time of 90 minutes with ability to reach -140°C/-220°F
-
Use electric refrigeration systems to cool the chamber.
Selling Points:
-
Safety: No handling of cryogenic gasses
-
Consistency: Can provide a more consistent cooling experience without the need for refueling.
-
Operational Costs: No need to purchase liquid nitrogen regularly; electricity costs can be lower in the long run.
-
Ease of Use: Typically easier to operate with less maintenance and fewer safety protocols required.
Things to Consider:
-
Higher Initial Cost: Has a higher initial purchase cost due to the complex refrigeration systems.
-
Slower Cooling: Needs 90 minutes heads up to reach -140°C/-220°F as compared to nitrogen-cooled chambers.
-
Electricity Dependency: Require a stable and sufficient electrical supply, which can limit their placement and use in some locations.

Summary
-
Nitrogen-Powered Chambers: Ideal for rapid cooling and lower initial costs but come with ongoing costs and safety guidelines..
-
Electric Chambers: Offer safety and operational ease with potentially lower long-term costs, but have higher upfront costs and slower cooling times.
The choice between the two types depends on factors like budget, safety protocols, intended use, and availability of resources (liquid nitrogen vs. electricity).
Book an introductory 30 minute call with our agents so that we can help you make the right decision for your business.
USA: https://meetings.hubspot.com/connor-beaudoin
MENA: https://meetings.hubspot.com/alexandru-toncu




