NAD+ Levels Relate To Physical Activity in Humans
New research suggests that NAD+ levels correlate not only with age, but with physical activity. In a study published by Nature Aging, researchers believe that a clear association between NAD+ levels and health status exists in human aging, with levels of NAD+ in older adults who exercised similar to those found in younger individuals.
But before we go any further. What is NAD+?
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD) is an organic molecule contained in every cell of the human body. As a “helper” molecule, NAD binds to and activates other enzymes that turn nutrients into energy, support metabolic health, and repair damaged DNA. Unfortunately, it’s been well established that NAD levels decline as you age, which could lead to metabolic disorders, brain fog, loss of energy, and the progression of various age-related degenerative disorders.
“Without NAD, life would cease to exist,” says Rhonda Patrick, Ph.D. of Found My Fitness.
This new study analyzes what happens with NAD+ in our muscles as we age. The researchers recruited 52 people, dividing them up into four groups: 12 young adults, aged 20-30, 17 older adults, aged 65-80 with normal levels of physical activity, 17 older adults with above-average levels of physical activity, and 12 older adults with low physical activity levels.
For reference, older adults with above-average levels of physical activity completed at least 3 one-hour exercise sessions a week for the last year, while adults with normal levels of physical activity were defined as having completed at least 1 one-hour exercise session per week. And those with low physical activity levels were defined as scoring under a 9 on the Short Physical Performance Battery Test.
In addition, both the young adults and the older adults with normal levels of physical activity averaged around 10 thousand steps daily. In comparison, older adults with above-average levels of physical activity were considerably more active, clocking more than 13 thousand daily steps on average.
The researchers then measured deep metabolomic analysis, recording the levels of more than a hundred various metabolites. NAD+ was among the metabolites most downregulated with aging. Not only were NAD+ levels correlated with aging; but they also depended on the amount of physical activity. While there was a considerable difference in NAD+ levels between the young adults and the normally active older adults, older adults with above-average physical activity were almost on par with the young group. The physically impaired older adults fared the worst, with the lowest levels of NAD+ recorded.
According to the study, “Most metabolic changes that occur with age in muscle can be reversed with regular exercise training.” And while this implies that NAD+ levels are linked to exercise, more research across a larger period of time would be beneficial. The end result of the study shows a correlation between NAD+ levels and amounts of physical activity.
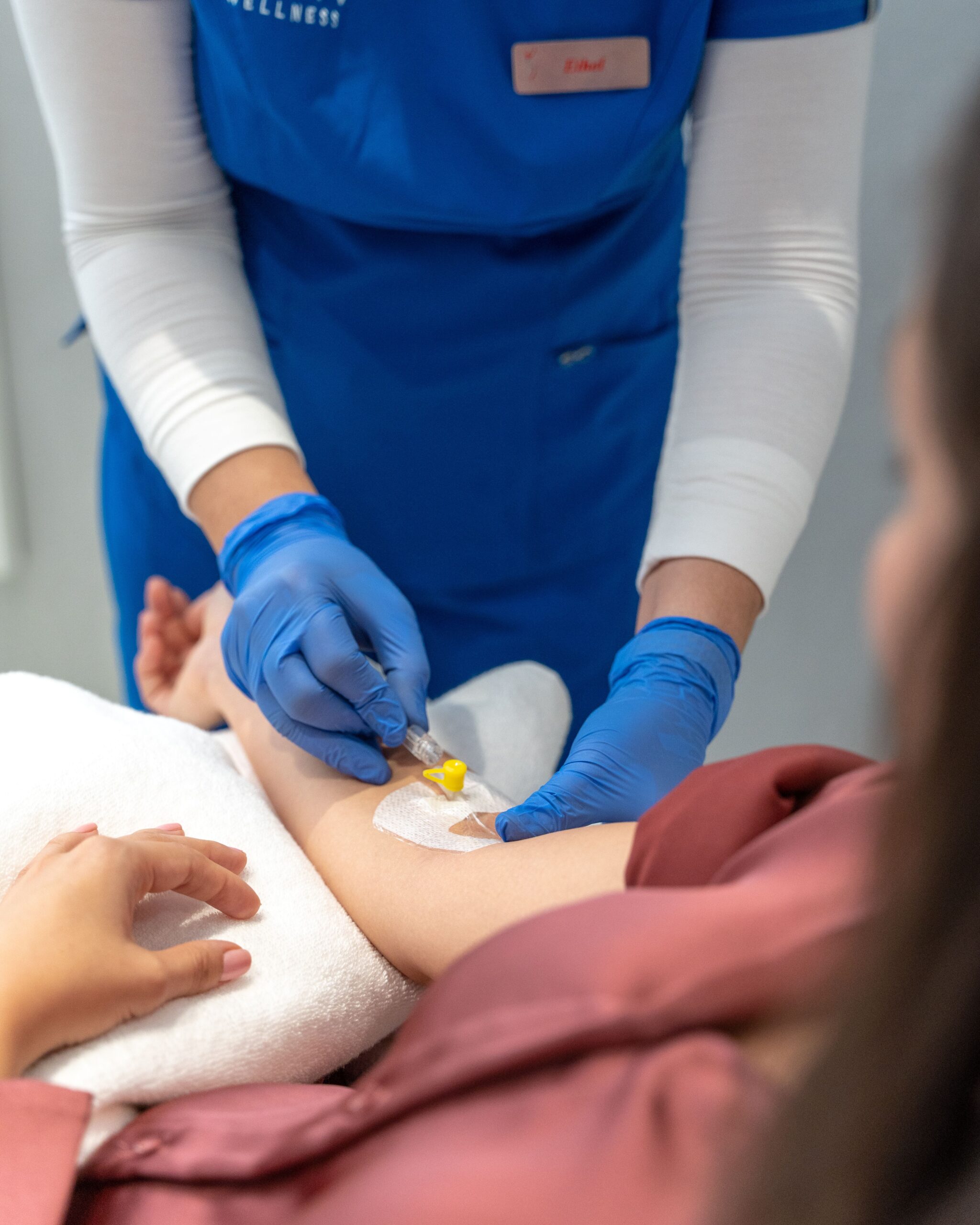
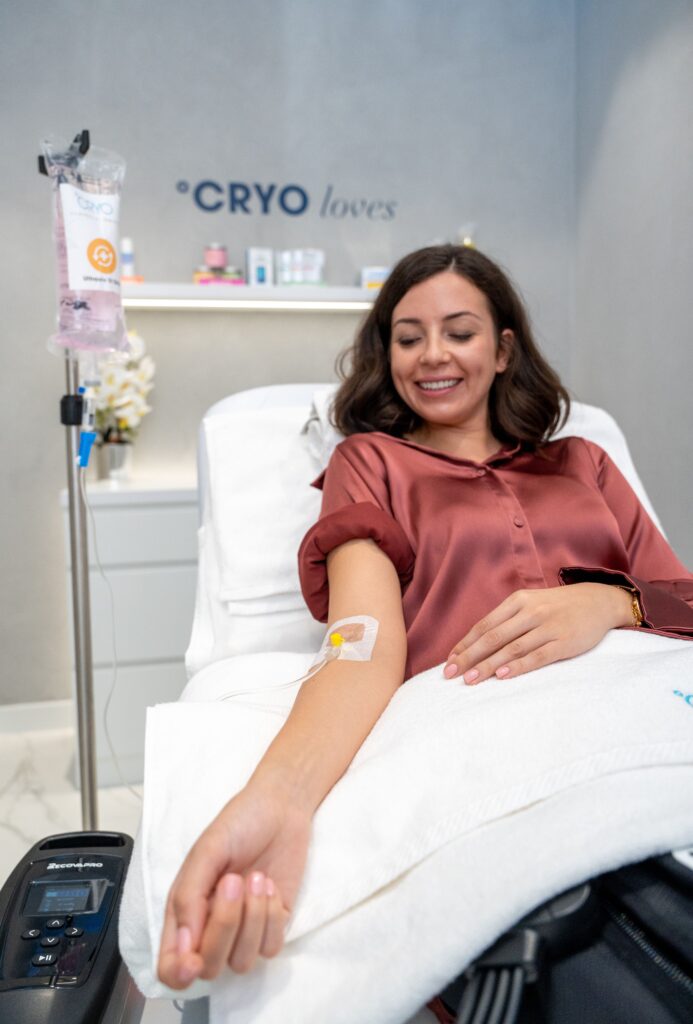
So, in theory, physical activity may help increase the levels of NAD+, at least in skeletal muscle. But in case you want to get a jump start on upping your NAD+ game, °CRYO’s NAD+ IV Drip Therapy may help fight signs of aging, support cellular health, and boost mood and energy.
NAD+ Drips is now available at °CRYO UAE Centers!